Linear and Binary Search Algorithms Explained
Here we try to demystify the two most common search algorithms-linear and binary search algorithm
Table of contents
- Linear or Sequential Search
- Linear Search Algorithm Steps Explained
- Code Implementation in Python
- Code Implementation in JavaScript
- Time Complexity Analysis
- Binary Search Algorithm
- Binary Search Algorithm Steps Explained
- Code Implementation in Python
- Code Implementation in JavaScript
- Time Complexity Analysis
- Conclusion
We often encounter challenges in computer science where a search algorithm has to be implemented to solve a specific problem. For example, finding a specific student's name in a list of students, finding a location on a map using coordinate values, etc.
Simply put, a search algorithm is a concept in computer science that is implemented to find specific data in a collection of data by following a series of well-defined steps. There are several search algorithms out there including; linear search, binary search, jump search, interpolation search, Fibonacci search, sublist search etc. Usually, the algorithm of choice is dependent on the data structure of the dataset we are working with, and also the time and space complexity.
For this article, our focus will be on the first two common search algorithms; linear and binary search algorithms. Here, we try to explain the concepts, code implementation in python and javascript and also briefly look at their time complexity analysis.
Linear or Sequential Search
The algorithm as the name implies iterates through the members of a list from the start to the end or until the target is reached; whichever comes first.
Our case study here will be an array of numbers. We perform the search on the array to output the index of the element otherwise return "Target not found".
Linear Search Algorithm Steps Explained
Identify our list and target
Starting from index 0, compare the value with the target
Return index if the element is found to be equal to the target
Otherwise, return "Target not found".
Code Implementation in Python
def linear_search(arr, ele):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == ele:
return i
return "Number not found"
numbers = [2,3,4,5,2,3,8,6]
print(linear_search(numbers,5)) #This expression returns 3 which is the index of the value 5
print(linear_search(numbers,15)) #This expression returns "Number not found"
Code Implementation in JavaScript
let number = [2,3,4,5,2,3,8,6]
function linearSearch(arr, ele) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === ele) {
return i;
}
}
return "Number not found";
}
linearSearch(number,5) //This expression returns 3 which is the index of the value 5
linearSearch(number,15) //This expression returns "Number not found"
Time Complexity Analysis
We will consider three main cases for the time complexity.
- If our target is found at the beginning of our array, the complexity is O(1) and is considered as the best-case scenario.
- If the target is found at the midpoint, the complexity is O(N/2) being the midpoint of the array.
- And for the worst-case scenario which is the true representation of the Big O Notation, the target found at the end of the loop or not in the array at all, complexity is O(N).
Binary Search Algorithm
This algorithm applies the divide and conquer rule to our search and can only be applied to a sorted array. This does a heavy lift for us and is a much faster way of implementing a search algorithm as we will find out why pretty soon.
Binary Search Algorithm Steps Explained
- Compare the middle element of our sorted array with the target value
- Move right if the target value is greater than the middle element and the search continues in that direction
- Or else move left if the target value is less than the middle element and continue in that direction
- Repeat the process until the middle element is equal to our target value or the target is not in the array
- Print the index of the target value if found or return the text string "Number not found" otherwise
Code Implementation in Python
def binary_search(arr, ele):
start = 0
end = len(arr)-1
while start <= end:
mid = start + (end-start)//2
if arr[mid] > ele:
end = mid-1
elif arr[mid] < ele:
start = mid+1
else:
return mid
return "Number not found"
numbers = [12,13,24,25,32,36,38,40]
print(binary_search(numbers,36)) #This expression prints 5
print(binary_search(numbers,76)) #This expression prints "Number not found"
Code Implementation in JavaScript
const binarySearch = (array, target) => {
let startIndex = 0;
let endIndex = array.length - 1;
while(startIndex <= endIndex) {
let middleIndex = Math.floor((startIndex + endIndex) / 2);
if(target === array[middleIndex]) {
return console.log("Number found at index " + middleIndex);
}
if(target > array[middleIndex]) {
console.log("Search right of array")
startIndex = middleIndex + 1;
}
if(target < array[middleIndex]) {
console.log("Search the left of array")
endIndex = middleIndex - 1;
}
else {
console.log("Not Found in this iteration.")
}
}
console.log("Number not found");
}
number = [12,13,24,25,32,36,38,40]
binarySearch(number,25)
binarySearch(number,55)
Time Complexity Analysis
The best case is when the target is found at the middle of the array, complexity is O(1) while the worst case is when the target is found far away from the middle, so complexity is O(logN)
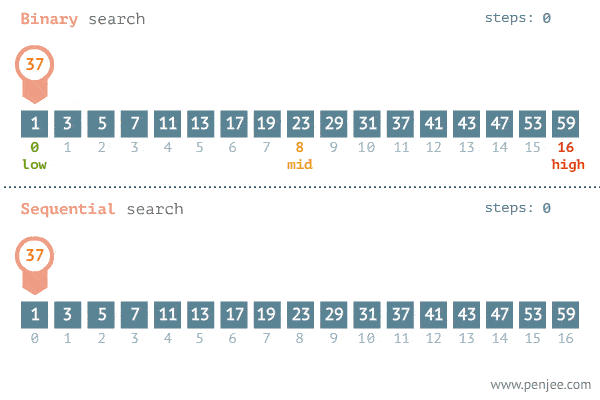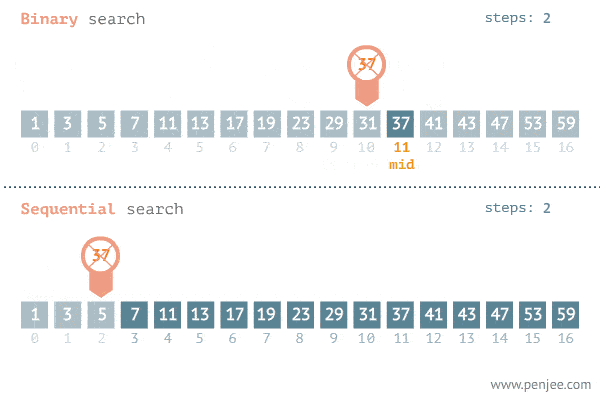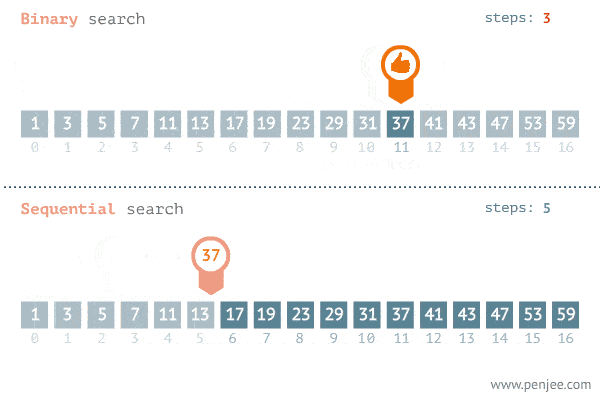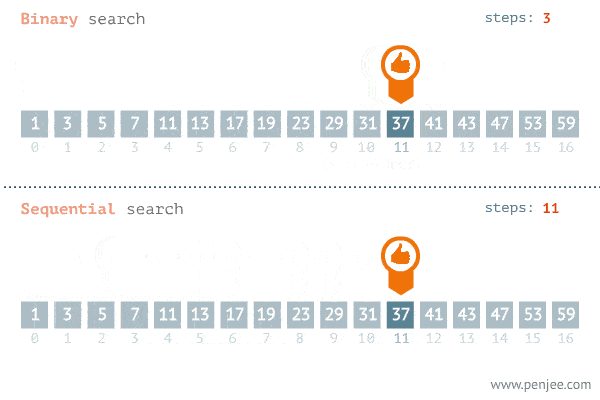 The Search Algorithm Gif(Fig: 3)
The Search Algorithm Gif(Fig: 3)
Conclusion
We looked at the linear and binary search algorithm and their code implementation in both python and javascript. We also looked at their time complexity analysis/Big O notation. The Search Algorithm Gif(Fig: 3) above gives up a graphical illustration of how both algorithms work

